Navigating the HS Code Maze: A Deep Dive into smartphone Classification
The Harmonized System (HS) code, a globally recognized classification system, plays a pivotal role in international trade, especially for complex devices like smartphones. Accurately assigning the correct HS code is crucial for importers and exporters, impacting tariff rates, regulatory compliance, and overall supply chain efficiency. Misclassification can lead to hefty penalties, shipment delays, and legal complications. This article explores the intricacies of smartphone HS code classification, delving into the relevant subheadings and the factors influencing their selection.
Understanding the HS System and its Structure
The HS code, developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO), is a six-digit nomenclature that categorizes traded products. This code acts as a universal language for customs authorities, facilitating trade data collection and standardization. The complete HS code can be further extended by countries to incorporate more specific product classifications, reaching up to 8 or 10 digits.
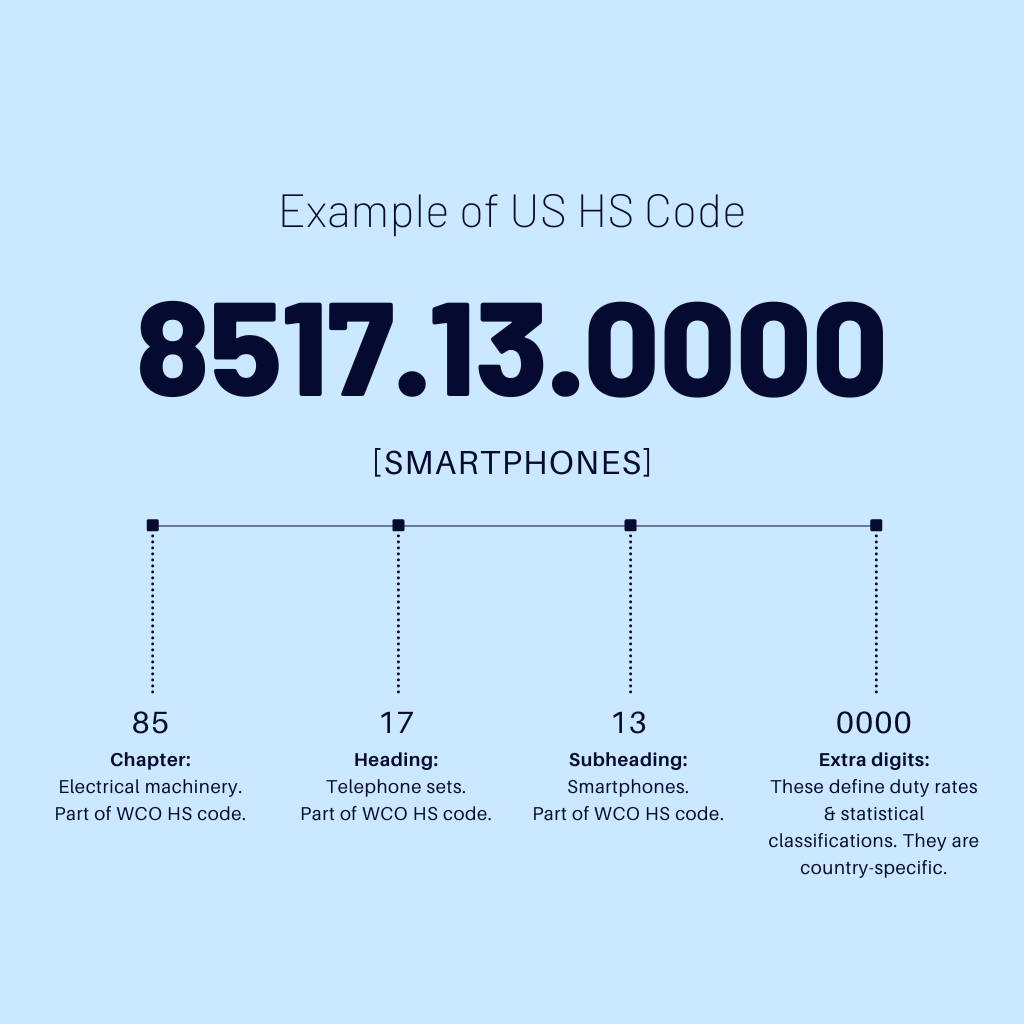
The HS code is organized hierarchically, with broader categories at the beginning and progressively finer details at each subsequent digit. The primary section related to smartphones is Section XVI: Machinery, mechanical appliances; electrical equipment; parts thereof; sound recorders and reproducers, television image and sound recorders and reproducers, and parts and accessories of such articles.
Key HS Code Subheadings Relevant to Smartphones
Several subheadings within Section XVI are pertinent to smartphone classification, often leading to debate and varying interpretations. Here’s a breakdown of the most significant:
8517: Telephone sets, including telephones for cellular networks or for other wireless networks; other apparatus for the transmission or reception of voice, images or other data, including apparatus for communication in a wired or wireless network (such as a local or wide area network), other than transmission or reception apparatus of heading 8443, 8525, 8527 or 8528.

This is the most widely considered heading for smartphones. It broadly covers telephones and other communication apparatus. Its significant subheadings are:
8517.12: Telephones for cellular networks or for other wireless networks.
This subheading specifically targets mobile telephones. It captures the primary function of smartphones as communication devices.
8517.62: Machines for reception, conversion and transmission or regeneration of voice, images or other data, including switching and routing apparatus.
If a smartphone’s data processing and routing capabilities are emphasized more than its telephony functions, this subheading might become relevant. However, utilizing this code is more complex as it focuses on network devices.
8471: Automatic data processing machines and units thereof; magnetic or optical readers, machines for transcribing data onto data media in coded form and machines for processing such data, not elsewhere specified or included.
While less common, some argue that smartphones, with their advanced processing power and data handling, could fall under this heading.
8471.30: Portable automatic data processing machines, weighing not more than 10 kg, consisting of at least a central processing unit, a keyboard and a display.
Although this sounds like a tablet with a keyboard, it could cause confusion, as some phones have displays and processing more powerful than early laptops.
Factors Influencing Smartphone HS Code Selection
Determining the precise HS code for a smartphone involves considering several factors, including:
Primary Function:
The core function of the device is paramount. While smartphones are multifunctional, their primary role as a communication device often leads to their classification under 8517.12. However, with increasing computational power and data handling capabilities, arguments for 8471 arise.
Technical Specifications:
The device’s technical specifications, such as its processing power, memory, camera capabilities, and wireless communication protocols, influence classification decisions.
Intended Use:
Understanding the intended use of the smartphone, whether primarily for communication, entertainment, productivity, or specialized applications, can guide the classification process.
Regulatory Requirements:
Different countries may have specific regulations and interpretations concerning smartphone classification, necessitating careful consideration of local customs rules.
Case Law and Customs Rulings:
Previous customs rulings and court cases can provide valuable insights into how similar devices have been classified, guiding importers and exporters.
Challenges in Smartphone HS Code Classification
The convergence of multiple functionalities in smartphones creates significant challenges in HS code classification. Key challenges include:
Multifunctionality:
Smartphones encompass communication, computing, multimedia, and navigation capabilities, making it difficult to pinpoint a single primary function.
Rapid Technological Advancements:
The rapid pace of technological innovation constantly blurs the lines between device categories, requiring frequent re-evaluation of HS code classifications.
Divergent Interpretations:
Customs authorities in different countries may interpret the HS code differently, leading to inconsistencies and trade disputes.
Evolving Case Law:
With new smartphone functionalities being rolled out constantly, the existing case law might be outdated quickly, generating new rulings.
Best Practices for HS Code Compliance
To ensure accurate HS code classification and compliance, importers and exporters should adopt the following best practices:
Thorough Product Analysis:
Conduct a comprehensive analysis of the smartphone’s functionalities, technical specifications, and intended use.
Consultation with Customs Experts:
Seek guidance from experienced customs brokers or trade consultants to ensure accurate classification.
Review of Customs Rulings and Case Law:
Stay updated on relevant customs rulings and court cases to understand prevailing interpretations.
Maintaining Detailed Documentation:
Maintain meticulous records of product specifications, technical data, and classification decisions to support customs declarations.
Proactive Communication with Customs Authorities:
Engage in proactive dialogue with customs authorities to address any uncertainties or potential classification disputes.
Conclusion
Smartphone HS code classification is a complex and nuanced process, demanding a deep understanding of the HS system, technical specifications, and regulatory requirements. Accurate classification is essential for ensuring smooth customs clearance, minimizing trade costs, and avoiding legal complications. With the continuous evolution of smartphone technology, ongoing dialogue and collaboration among customs authorities, industry stakeholders, and trade experts are crucial for maintaining consistent and accurate classification practices. By adhering to best practices and remaining vigilant in monitoring regulatory developments, businesses can effectively navigate the HS code maze and ensure compliance in the dynamic world of international smartphone trade. This diligence will prevent trade friction and assist in the streamlined flow of innovation around the world.



